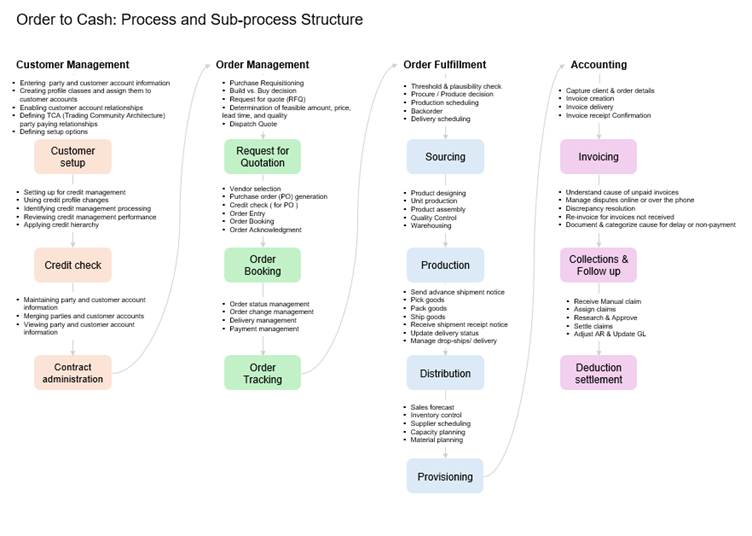
Key Challenges in O2C
O2C is one of the most complex general and administrative (G&A) processes, typically comprising about 1 to 3 percent of revenue. Because O2C touches multiple functions, ranging from commercial and sales to finance, legal, and customer support, cross-functional alignment is critical to fully understand what is happening in the O2C process—yet difficult to achieve. Higher costs, inefficiency, and margin leakages aren’t the only effects of siloed functions. As a customer-facing process, O2C has a significant effect on customer experience, as well as revenue growth. Trained by their experiences as consumers, business customers increasingly want a touchless order experience, with little hands-on interaction across the ordering process. They want continual notifications and real-time updates on order status, and they expect disputes to be extremely rare and quickly resolved when they occur. These expectations translate to new strains on existing O2C processes as B2B businesses adapt to newer business models, such as providing B2C-like e-commerce experiences through online ordering, or responding to the subscription-based sales.
Advanced Strategies for O2C Optimization
Digging deep into the process and underlying data means applying advanced process-mining data analysis on ERP transaction data to analyze O2C processes. By uncovering consistent patterns of errors and rework, revenue leakage, and customer-experience pain points, the tools generate insights that previously had been impractical to achieve because of data limitations. Order intake is broken down into first time-right orders, unfulfilled or on-hold orders, and average days to confirmation. Shipment is viewed in terms of perfect order delivery. Invoicing is analyzed for invoicing errors and average days to issue an invoice. Payment is viewed in terms of short payments written off as bad debt. All dimensions are evaluated across the three dimensions of efficiency, revenue leakage, and customer experience.
Data-Driven Insights with SAP Analytics Cloud
SAP’s Order-to-Cash process solutions, coupled with the SAP Analytics Cloud, offer unparalleled insights into transaction lifecycles. By harnessing process-mining capabilities, SAP allows businesses to uncover inefficiencies, identify revenue leakages, and address customer pain points. These solutions enable organizations to:
- Analyze order accuracy and fulfillment times.
- Detect patterns leading to invoicing errors or delayed payments.
- Enhance customer satisfaction through real-time order tracking and dispute resolution.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies
Organizations are elevating their O2C processes by adopting:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Predict payment delays, automate routine tasks, and generate actionable insights.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Streamline repetitive operations such as invoice creation and credit approvals.
- Blockchain Technology: Securely track transactions and establish transparency, reducing disputes and improving trust.
Unified Accountability with SAP S/4HANA
SAP’s S/4HANA platform ensures seamless integration across sales, finance, and customer service, enabling real-time data access and operational transparency. By implementing a unified O2C framework, organizations can achieve faster order processing and minimize customer touchpoints.
To address these issues, organizations should deploy internal process and tech fixes, such as digitizing the order process, imposing order rigor, streamlining order holds and credit-check processes, and ensuring robust validation and monitoring. Appointing global process owners to drive accountability is crucial—particularly by building a common interface for customers, with minimal touchpoints. When O2C processes reside in disparate functional silos, with no single point of accountability for customers, they tend to break down: throughput times become longer, with too many customer touchpoints.
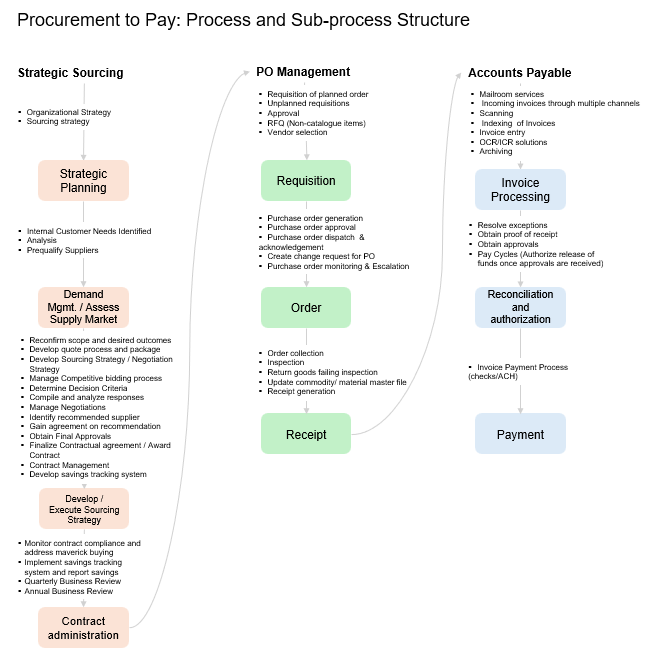
Procure-to-Pay (P2P): Optimizing Procurement for Cost and Efficiency
The Procure-to-Pay (P2P) process is integral to managing supplier relationships, controlling costs, and ensuring smooth procurement operations. It encompasses activities from identifying procurement needs to processing payments, making it critical for financial governance and supply chain resilience.