Introduction
In the complex world of Retail and CPG, there are hundreds of applications necessary to keep the various and interdependent operations running. Amid the continuous, tumultuous, and dynamic progression of these activities, it is normal to witness phases of expansion, adaptation, and innovation, which reflect the obsolescence of some applications and the introduction of new and more advanced solutions capable of rigorously and effectively responding to market demands.
This is where global companies encounter the coexistence of legacy and new applications, often having to manage relationships with various vendors and navigating a complex conglomerate of unique relationships and dynamics that frequently require exceptions and compromises. A situation that’s often considered challenging for modern organizations striving to centralize application management, providing L1, L2, and L3 support efficiently on a local level while also introducing a global and highly professional perspective on Application Management Services (AMS).
Recent studies on digital transformation highlight that AMS in RCG industries achieve up to 45% operational cost reduction through AI and machine learning-driven automation, as well as cloud-native solutions. Integrating reinforcement learning algorithms into AMS enhances real-time decision-making for high-priority incidents, minimizing downtime and improving SLA adherence.
However, moving in this direction, relying on a single partner for those starting from a fragmented and complex landscape, represents a significant challenge. The partner must demonstrate technical expertise, reputation, and resources on a global scale, in addition to understanding and recognizing the specific needs and challenges that the industry player faces in the intricate interplay between technology and business.
This document outlines a comprehensive framework for leveraging AMS to drive operational excellence and innovation within the RCG sector. By focusing on advanced automation, risk mitigation, and alignment with business objectives, Cognizant empowers enterprises to achieve cost efficiency and sustained growth, blending the formidable combination of industry and technology expertise.
Core Components of AMS in RCG
Cognizant’s AMS framework begins with a deep understanding of the application and technology landscape, ensuring tailored solutions for diverse business requirements.
1. Application Inventory and Technology Landscape
AMS success starts with mapping the existing application portfolio, categorizing them by complexity, business criticality, and dependencies. This enables prioritization of high-impact areas.
2. Volumetric Data Analysis
Using six months of ticketing data (incidents, service requests, change requests, problem management), AMS teams are able to forecast demand and optimize resource allocation, ensuring high SLA performance.
3. Geographic Coverage and SLA Management
Retail and consumer brands often require 24/7 support with region-specific nuances. Cognizant’s global delivery model ensures seamless support through strategically located hubs.
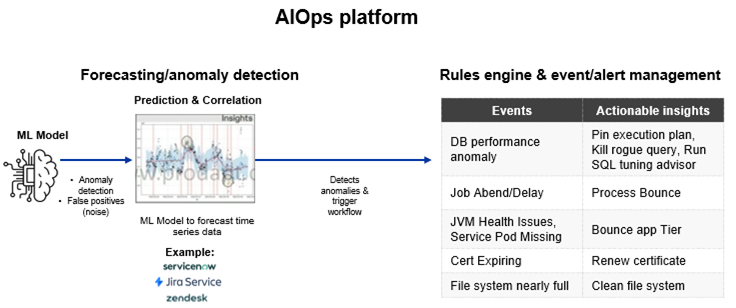
4. Automation and AI Integration
Automation drives efficiency, reducing manual efforts and enabling real-time issue resolution. AI-powered tools like Bluebolt™ and Neuro™ enhance problem-solving and enable predictive maintenance.
Even though these four points represent the backbone of a strategic transformation where technology, deep industry understanding, and specific account landscape knowledge must converge to realize a broader multi-year blueprint plan, trust and transparency between the involved parties are undoubtedly the most crucial steps to ensure a successful outcome.
Risk Mitigation and Transition Strategies
Transitioning AMS operations involves inherent risks. Cognizant employs a robust, phased approach to minimize disruptions while ensuring operational continuity.
1. Criticality Analysis and Contingency Planning
By identifying critical applications and potential risk factors (e.g., aging infrastructure, vendor dependencies), Cognizant develops tailored contingency plans to address high-risk scenarios.
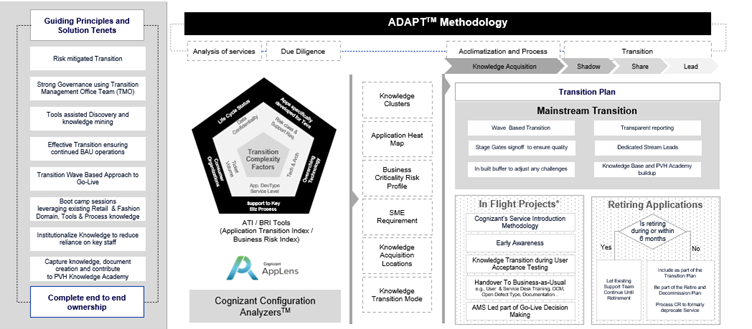
2. Transition Plan and Cognizant Accelerators
Using the ADAPT methodology, Cognizant ensures minimal disruption through structured governance, staggered waves, and accelerators like Bizagi Modeler and Configuration Analysis Tools. The result is a transition plan that encompasses mainstream, in-flight projects, and retiring applications, combined with ATI/BRI analysis (Application Transition Index/Business Risk Index).