Introduction
The retail and consumer goods industries are constantly experiencing transformation, driven by evolving consumer expectations, technological advancements, and market volatility. In this dynamic environment, Business-as-a-Service (BaaS) has emerged as a game-changing paradigm, offering unparalleled flexibility, efficiency, and scalability. This thought leadership document explores the power of BaaS in revolutionizing operations and driving growth in the retail and consumer goods sectors.
What Is Business-as-a-Service?
Business-as-a-Service (BaaS) is a comprehensive model that allows companies to outsource entire business functions or processes to specialized service providers. Unlike traditional outsourcing or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models, BaaS offers end-to-end management of business processes, including technology, people, and operations.
In the retail and consumer goods context, BaaS can encompass a wide range of functions, from supply chain management and inventory control to customer service and marketing analytics. This model enables businesses to focus on their core competencies while leveraging external expertise and cutting-edge technologies to drive operational excellence.
The Retail Landscape Today
Retail and consumer goods companies face distinct challenges, including supply chain inflation, increasing customer expectations, and the pressure to deliver seamless omnichannel experiences. The BaaS model mitigates these challenges by offering cost-effective, scalable solutions tailored to specific industry needs. BaaS enables access to the latest technology and capabilities without the high cost of ownership, allowing companies to adapt quickly to seasonal peaks, rapid shifts in demand, and fluctuating economic conditions.
BaaS empowers companies to rethink operational efficiencies in areas such as inventory management, fulfilment, and customer engagement.
Many retailers, from regional chains to multinational corporations, are grappling with a common set of challenges:
- Financial Pressures: Despite steady or even growing revenues, numerous retailers are experiencing shrinking profit margins or outright losses. This financial strain is often the result of multiple factors converging simultaneously.
- Massive Investments: Companies are pouring significant resources into modernizing their operations. These investments span various areas such as store renovations and format changes, E-commerce platforms, Supply chain optimization, and IT infrastructure overhauls.
- Changing Consumer Behaviour: Shoppers are becoming more price-sensitive and discerning. Many are buying fewer items, opting for cheaper alternatives, or shifting to different shopping channels altogether.
- Cost Absorption: To remain competitive and maintain customer loyalty, many retailers are absorbing increased costs from suppliers rather than passing them fully to consumers.
- Digital Transformation Challenges: The implementation of new technologies, while necessary, often comes with unforeseen complications, extended timelines, and budget overruns.
The Need for Innovation in Retail
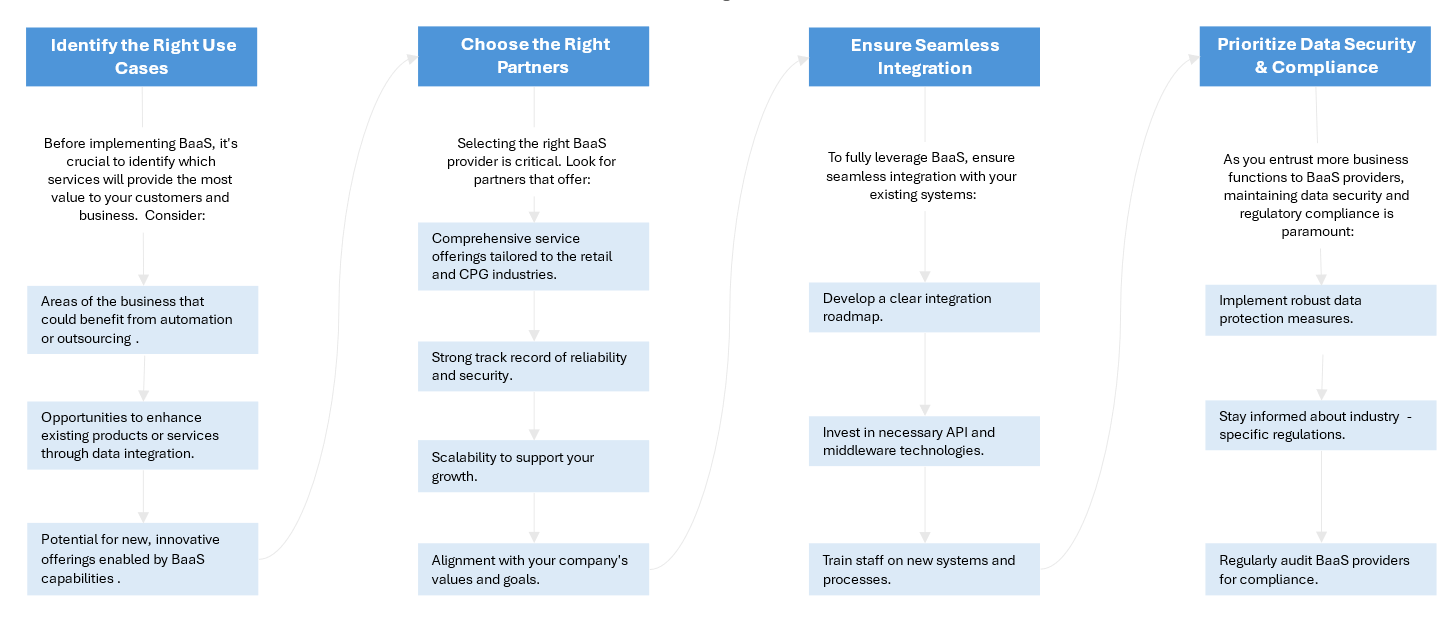
In this context, Business-as-a-Service (BaaS) emerges as a potential solution to many of these industry-wide challenges. BaaS offers retailers the opportunity to:
- Enhance Operational Efficiency: By leveraging cloud-based solutions and expert management, retailers streamline their operations without the need for massive in-house investments.
- Improve Agility: BaaS enables quicker adaptation to market changes and consumer trends, allowing retailers to respond more effectively to shifts in shopping habits.
- Optimize Cost Management: With BaaS, retailers better control costs by paying only for the services they use, potentially mitigating financial strain.
- Access Advanced Technology: BaaS providers offer state-of-the-art technologies without the need for significant upfront investments or the complexities of in-house implementation.
- Focus on Core Business: By outsourcing complex technical and business processes, retailers concentrate on serving customers and developing products – their true areas of expertise.
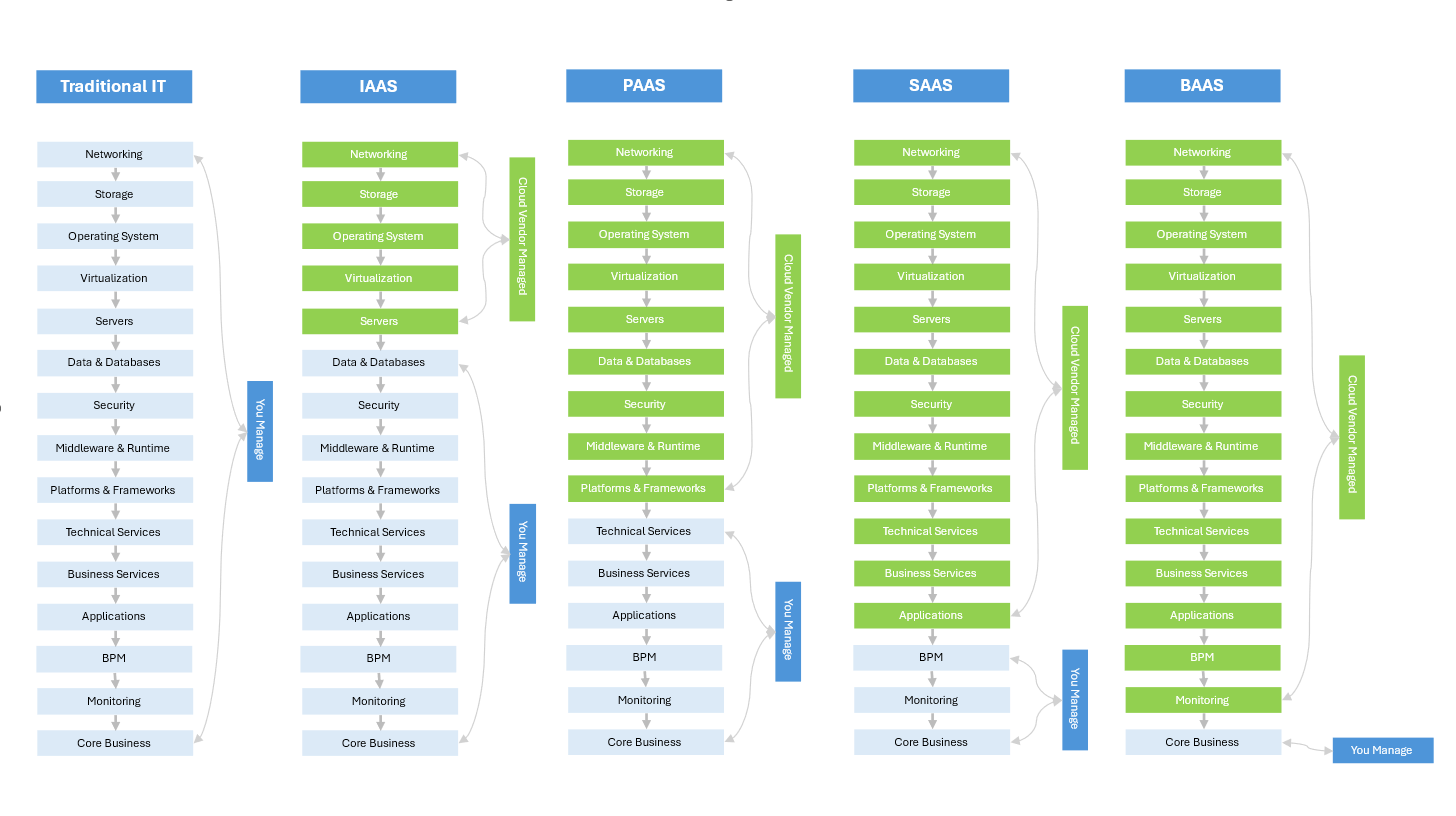
From Legacy to Agility
The journey from traditional IT infrastructure to BaaS represents a significant shift in how businesses operate. This evolution has progressed through several stages: